Societal Security and Social Harmony
Societal Security was introduced for “the first time by the Copenhagen School as a dimension of national security” (Navidnia, Manijeh; 2009),
but by welcoming the emerging security, different experts of humanities took part in its theoretical processing and thus, the conceptual range of societal security has encompassed an extensive domain that is still no determinate theoretical consensus about it.
In this regard, sociology is one of claimants and has an enlightening role in expression of societal security.
Sociology by portraying today world as a world where every day the number of its bullets, guns, and weapons are increased, a world where gap between rich and poor becomes deeper every day, a world where young and old, male and female, child and adult, do not get rid of the injustice, is faced with the question can a security be established without regarding inequality, bullying, and hegemony?
The world whose technical and technological advances continue to surprise people, why is sometimes unable to maintain the most basic aspect of security that is “life safety”?
Sociology’s response can be summarized in dichotomization of world, when humans are divided into two fronts friend and enemy, rich and poor, powerful or weak, wise and fool, valid and invalid.
Dichotomized world, by making contrast between full wealthy class and completely poor class, is a barrier to understand the beautiful sights of people, to understand different people and to interact with diverse groups of human and this makes people to easily consent to the destruction of human beings and killing each other and “the present century is characterized by insecurity”(Giddens, Anthony; 1991).
Therefore, from a sociological perspective, the production of and processing security is not possible regardless of social context and policy is just one aspect of security by ending its monopoly, the multiple dimensions of security can be realized (Navidnia, Manijeh; 2006).
On the other hand, increasing opposition between the government and the people has revealed a deep gap between security of public and national security and it has left no way to legitimate justification of seizing power and force tools by governments.
Therefore, rethinking security could be posed in the form of a new discourse as “societal security” that is based on principles such as being people-centered rather than state-centered (general-based rather than specific-based), being human-oriented rather than power-oriented, equality rather than hegemony.
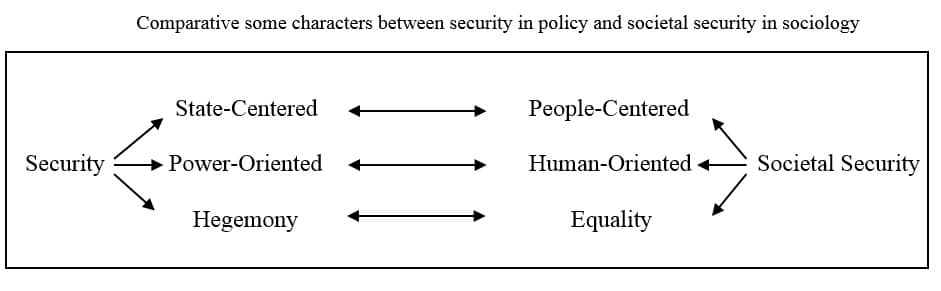
Thus, societal security addresses the establishment of security for a diverse range of small and big units in under-national, national and international levels.
Units are considered in the form of family, ethnicity, political parties, voluntary organizations, youth, women and children, arts and cultural groups, religious groups, racial groups, citizens, the neighborhood, business and occupational groups and others, but what makes them a reference object to societal security is government oppression, legal discrimination, social inequalities (such as the level of access to education, occupation and income), lack of access to life facilities (such as health, food and etc.);
these matters made it difficult for them to continue their life and perhaps in some cases, their physical body is not targeted, but their spiritual existence as honorable beings is to fall and collapse (Navidnia, Manijeh; 2003).
In fact, references object of societal security (security for whom?) are various groups who live with fears, concerns, threats and vulnerability and they suffer from insecurity.
Because their identity and social being is subject of discrimination and they don’t have enough freedom to protest, they are prevented from dissemination of their ideas and beliefs, and there are no strong executive laws according to them they could prove their identity and their credit and restore their rights.
From the perspective of sociology, societal security rather than relying on measures of military power, is established in functional processes by regular society forces.
Therefore, security in sociology is detached from political hegemony and decisions of the government elite and will be close to social harmony and common norms.
In fact, societal security by believing in principle that every various religious, artistic, racial, national, sexual and other groups are beautiful, colorful and different pieces of human life which together form human society garden provides the proper communication between different groups and thereby provides the social harmony and integration (Navidnia, Manijeh; 2010).
With the establishment of societal security, social groups and units assure of continuing their life and access to resources and facilities, and risks and threats of aggression and invasion to their material and spiritual existence would end and thus, no reason will be left for conflict and aggression between them and social harmony will realize (Navidnia, Manijeh; 2006).
But on the other hand, if social units follow the behavior patterns of cooperation and friendship, they would realize social harmony that facilitates the societal security mechanism.
So we can consider that there is mutual relationship and convergent interactions between societal security and social harmony.
Reference:
1- Navidnia, Manijeh (2009) “Societal Security“, Tehran: Research Institute of Strategic Studies, p.84.
2- Giddens, Anthony (1991) “The consequences of modernity” , Stanford University Press, p.171.
3- Navidnia, Manijeh (2010) “ Security Priorities of Citizens in Various Zones of Tehran“ Tehran, Quarterly Journal of Human Geography, Vol. 2, No. 2, p. 87-100.
4- Navidnia, Manijeh (2006) “Theoretical Consideration on Societal Security with Emphasis on Types of Security”,Tehran, Strategic Studies Quarterly, Research Institute of Strategic Studies, Vol. 9, No. 1, p. 53-72.
5- Navidnia, Manijeh (2003) “ An Introduction to Societal Security“,Tehran, Strategic Studies Quarterly, Research Institute of Strategic Studies, Vol. 6, No. 1, P. 55-76.
Publish on: http://www.peacefromharmony.org/?cat=en_c&key=503