The Principle of Sphere Societal Security
Phases of Societal Security realization and its facing issues
When it comes to talk about Societal Security, the aim is describing the living conditions of all people with comfort and convenience. To achieve this, some multiple and complex mechanisms are necessary that can be addressed in terms of “security cycle”.
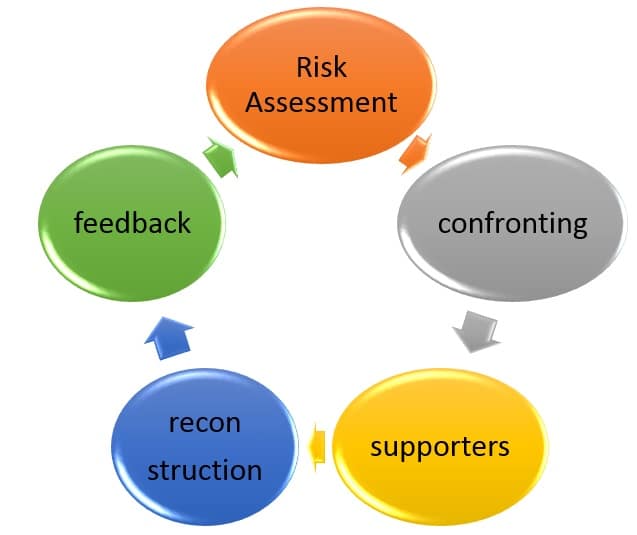
Security cycle consists of five phases: risk assessment, confronting ability, support level, reconstruction power, and performance feedback. In this paper, in order to study the problems of Societal Security realization, the five phases of this cycle are discussed.
Introduction
After more than two decades, there is not yet any consensus on Societal Security and two components of security, “Reference object” and “threat type” is not yet formulated. Copenhagen school considers social groups as reference object and focuses on threat to identity.
After that, the authors have shown a greater focus on Societal Security and assume social vulnerability as threat to social security.
If we accept that a society or a community is made up of a series of individuals who have their interactions and relationships in specific areas such as family, school, department, so we can consider these interactive spaces as reference object of Societal Security and we can talk about Societal Security of family and so on.
Risks also include all of the problems and shortcomings that obstruct the natural flow of the interactive space and make its development impossible. Hence, social damages
Can be one of the fundamental threats to Societal Security. But problems such as discrimination, disrespect, lack of freedom of choice, discredit and so on are social aspects of threats that affect their interactions.
Regardless of the various perspectives on Societal Security, it should be noted that the securitization procedure has the same mechanism and cycle for all forms of security.
This cycle has 5 levels or phases and each level has various mechanisms and is a prerequisite for next levels.
The first phase is prediction and understanding of the extent and severity of the risk, the second is use of confronting and controlling strategies and its associated power tools, the third is taking advantage of the support forces and their aids, the fourth phase is preparation of conditions for the reconstruction and restoration of the risks and return to normal conditions and, finally, the fifth stage is performance feedback and evaluation.
Societal Security is not free of the security cycle and the implementation of these five steps, because realization of security is not possible without it.
Typically, Societal Security studies is based on one of these phases and there is no overall look on the cycle.
By briefly reviewing each phases, the present paper is intended to overall assess the problems of realization of Societal Security in the world. Obviously, in a brief process of such a large topic, lots of big and small issues are ignored.
Risk Assessment
Security is typically assessed by threats and risk components.
That is, how much risk is less (or more to control the risks) security realization is more probable, and vice versa.
With this approach, risk identification and estimation is very significant and important. Therefore, the first step for Societal Security would be risk assessment.
But because Societal Security has not a comprehensive narrative, this has caused everyone to have a different definition of Societal Security and its risks.
This paper ignores conflicts and dispersion of ideas and focuses on common points.
Assuming that according to many experts the social harms and deviations have targeted Societal Security, so the first step is understanding the harms and their levels as risk assessment.
So, firstly, it is necessary to have statistics related to damages. In this step, there are two major problems:
A – In many cases there is no statistical data, for example statistics about illegal abortion or hidden suicides.
B – In those cases in which there are data, inconsistencies between the figures make it impossible to have any realistic estimation.
Thus, lack of statistics or inconsistent statistics, has led to a have no clear vision of the risks and threats and no access to reality. This is especially significant in developing countries.
Confronting Ability
When the risk types are not specified and there is no accurate estimation of their extent and severity, confronting strategies and tools would be ambiguous as well.
Before, people thought drug addicts must go to jail, but now the advice is to send them to rehabilitation.
Here is the question which way is efficient to deal with addiction and achieving security in this context? The fact is there is no clear answer.
What should be done with prostitute women?
What should be done with street children?
What can be done with thieves and robbers?
And there is many similar questions with no obvious and unique answer for them.
It is obvious that confusion and uncertainty in determining the confronting patterns and behaviors and combatting damages, will lead to a decline in Societal Security.
Support level
Institutions and organizations are responsible for implementation and operationalize the plans and commands of Societal Security.
The first problem is that, unfortunately, there is no certain charge to Societal Security:
in some cases the police, in some cases social security, sometimes the Ministry of Health or the Ministry of Labor or Ministry of Education, and also religious institutions, and so on.
Here the problem is not the multiplicity of relevant organizations, but the problem is having no clear plan to show their duties towards Societal Security.
But regardless of this problem, Societal Security is isolated in the world, and don’t have nongovernmental organizations and public bodies.
NGOs and various associations can participate voluntarily to reducing costs and play effective role in providing innovative and people-friendly solutions.
Supporting forces are key players in success of security plans and measures.
More support of security operations from organizations especially people-centered and people-driven organizations, means more realization of security and vice versa, less in supporters means more challenges in security realization.
Unfortunately in developing countries, public institutions and non-governmental organizations are not on top levels of the executive and decision-making authority, and regarding the security (that government officials are more sensitive about it) this problem has been ignored.
Regarding Societal Security, this problem raise more concerns, because uncertainty of first step (understanding the risks) and second step (confronting and control) has caused serious damage at this level and neglecting this has led us to the question of who can support the uncertain plans of Societal Security?
Reconstruction power
Security measures attempt to reduce the risks and minimize damages to the people. However, the occurrence of some risks cannot be avoided and their damages will affect on people.
Thus, Societal Security needs measures and policies to repair the damage and to rebuild the current conditions.
This has been somehow realized in the case of addiction, such as public and private drug treatment centers attend drug users after release from the damage so they can come back to family and work.
Similarly, some kinds of insurance for home, car, goods or other property have the same role for repair the damages.
Also, some or psychiatric or counseling centers in addition to treatment, do psychological empowerment to return patient to his normal life. But unfortunately, the Societal Security has serious problems in this field that can be said in some cases it even didn’t think about the problems.
To prove this claim, only a few examples will be stated. What decisions has been made for security of children to offer measures for compensation and rehabilitation that should be taken.
What specific and clear measures have been taken about the security of women, youth, elders, or religious minorities and sexual minorities? In fact, there is no answer to it and hence it can be concluded that Societal Security still does not have a specific status in the world.
Performance feedback
Assuming that each of the four steps had been taken to achieve security, performance control and evaluation is the final step.
There must be some organizations in charge of providing assessment and evaluation about objectives, plans, practices, tools, actions and all those things that used to realize security
By accurate assessment based on scientific assessments, not ideological, a realistic estimate of plans and tasks would be achieved.
Thus, the strengths and weaknesses will be determined and shortcomings, obstacles, restrictions, disincentives and motivators are identified and then by this feedback, another cycle to achieve security will be defined and re- launch.
objectives, plans, practices, tools, actions and all those things that used to realize security. By accurate assessment based on scientific assessments, not ideological, a realistic estimate of plans and tasks would be achieved.
Thus, the strengths and weaknesses will be determined and shortcomings, obstacles, restrictions, disincentives and motivators are identified and then by this feedback, another cycle to achieve security will be defined and re- launch.
Societal Security shortcomings in its fulfillment cycle, also includes the lack of relevant authorities to assess performance and provide feedback.
There is no justified and legitimate group for assessing Societal Security cycle and every organization who consider it responsible for implementing some security plans, consider itself for assessing plans as well.
Conclusions
Societal Security that pursues peace and comfort for diverse groups and communities, from family and neighborhoods to human rights advocates at global level, needs “security cycle”.
But the cycle of Societal Security in the world, as said before, faces serious obstacles and to review it, some facts of each step are discussed. In the first step, in addition to differences in “risks type” (which is an important and key point), another problem is paradoxical information or lack of accurate statistics and data about present conditions and its related risks.
The second step is influenced by confusion about risk types and the extent and severity of threats and thus is not able to take appropriate measures to deal with risks and the control is more on people common and private life rather than combating the threats. In third step that requires the support from non-security forces, social security, regardless of the negligence of people power, is not able to get help from people because it has not been able yet to convince people to run its programs.
Repairing damages in the fourth phase is implemented upon the duties of some organizations including insurance and social security. Regardless the lack of coordination of these organizations with Societal Security plans, the other major problem is that many groups such as children and minorities are not included in security measures.
Finally, in fifth step that includes performance feedback there is no performance feedback by any organization outside of the security forces.
With regard to what was said, it can be concluded that Societal Security cycles is facing with fundamental problems and these problems are not only for developing countries and their situation, but it comes from negligence of the “Social Aspects of Security” at the global and international level.
Reference: Manijeh Navidnia (2009), The Principle of Sphere Societal Security, http://www.peacefromharmony.org/?cat=en_c&key=669



